内容纲要
map容器

map构造和赋值
功能描述:
- 对map 容器进行构造和赋值操作
函数原型:
构造:
map<T1,T2> mp;//map默认构造函数;map(const map &mp);//拷贝构造函数
赋值:
map& operator=(const map &mp);//重载等号操作符
void test()
{
map<int, string> mp1;
pair<int, string> p1(1, "张三");
pair<int, string> p2;
p2 = make_pair(2, 97);
//pair<int, string> p3 = make_pair(2, 97); 会报错,不存在int ---> string转换
// 但是上面拆开来创建就不会有问题。
//map容器的插入
mp1.insert(pair<int, string>(3, "张麻子"));
mp1.insert(p1);
mp1.insert(p2);
printMap(mp1);
map<int, string> mp2;
//map的赋值
mp2 = mp1;
}Summary:
map中所有元素都是成对出现,插入数据时一定要使用对组
map大小和交换。

map插入和删除

======================================================
- 《注意看,眼前的这个现象叫自动确定键值对》,
~当string在int类型前面的时候 它也依旧会依据int 来进行排序 ~。md我记错了,,不是根据value的值来排序,,下面这个图是根据拼音来排序的吧。。。。
例证
============================================
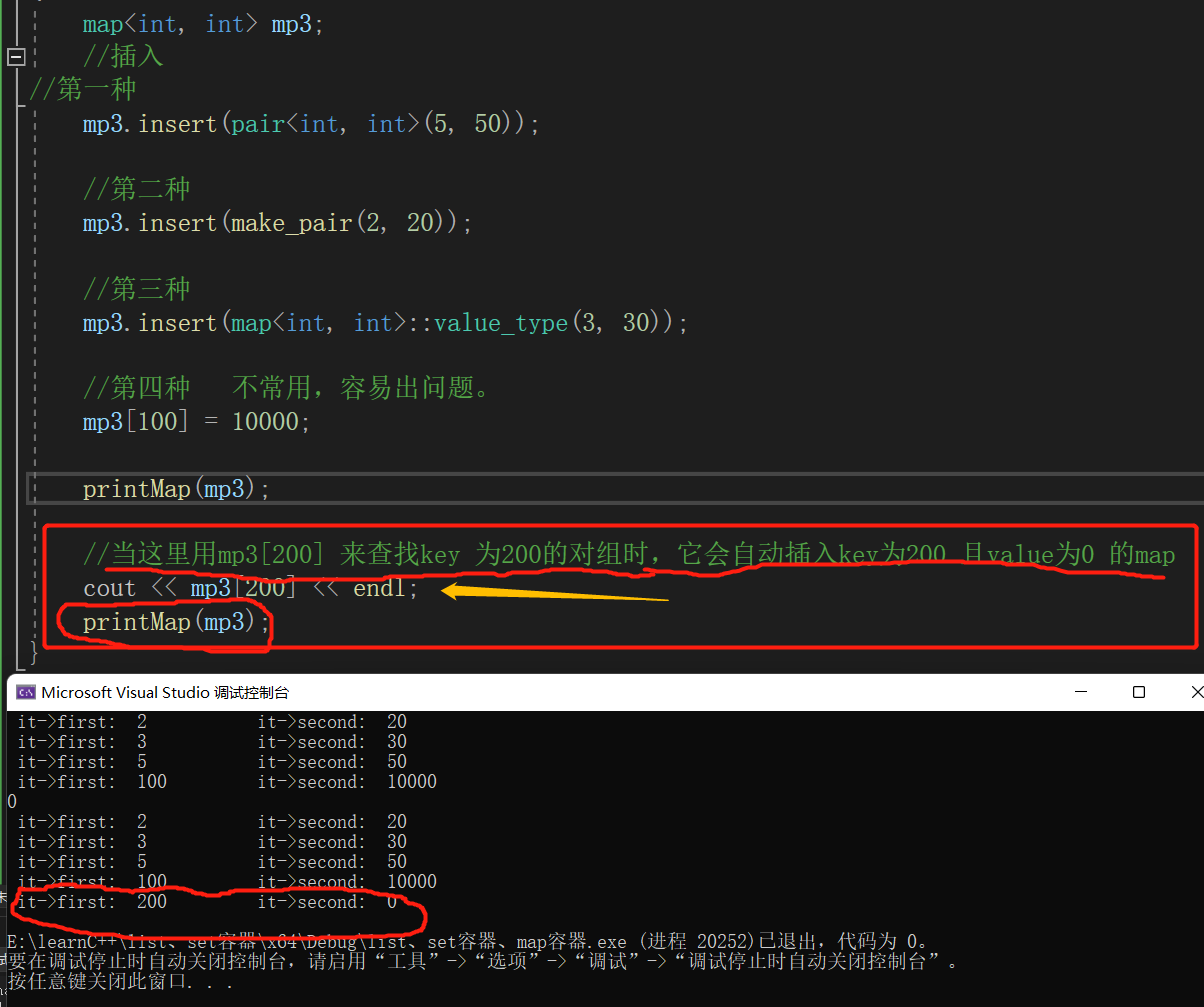
- 尽量不要用
mp1[100] = 10000;这种方式插入对组,因为哪怕是打印输出cout << mp1[200];的时候,它都会创建key 为200 ,value为0 的值。 如下图。
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
void printMap(const map<int,string> &mp)
{
for (map<int,string>::const_iterator it = mp.begin();it != mp.end();it++)
{
cout << " it->first: " << it->first << " it->second: " << it->second << endl;
}
}
void printMap(const map<int, int>& mp)
{
for (map<int, int>::const_iterator it = mp.begin();it != mp.end();it++)
{
cout << " it->first: " << it->first << " \t it->second: " << it->second << endl;
}
}
//map容器插入和删除
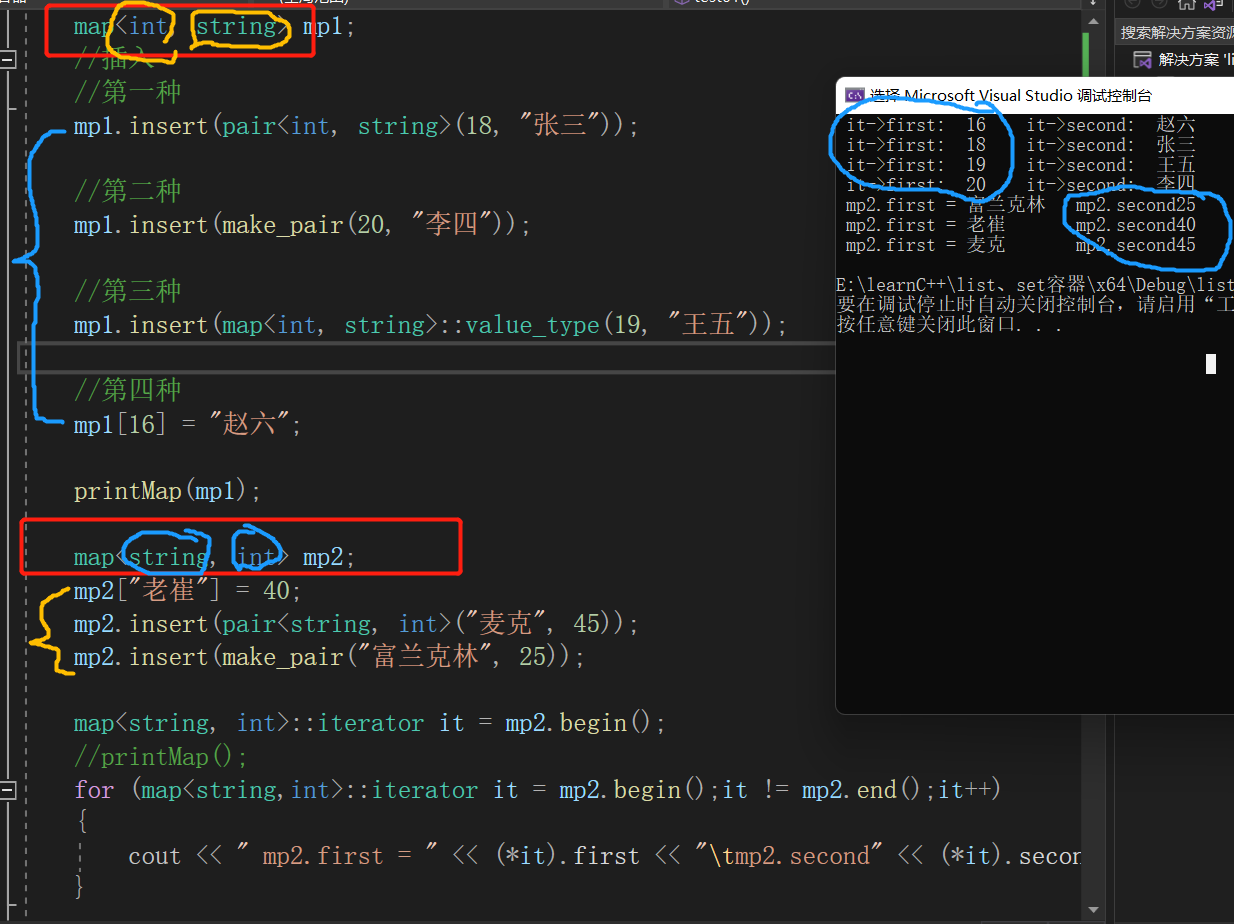
void test01()
{
map<int, string> mp1;
//插入
//第一种
mp1.insert(pair<int, string>(18, "张三"));
//第二种
mp1.insert(make_pair(20, "李四"));
//第三种
mp1.insert(map<int, string>::value_type(19, "王五"));
//第四种 不常用,容易出问题。
mp1[16] = "赵六";
printMap(mp1);
map<string, int> mp2;
mp2["老崔"] = 40;
mp2.insert(pair<string, int>("麦克", 45));
mp2.insert(make_pair("富兰克林", 25));
map<string, int>::iterator it = mp2.begin();
//printMap();
for (map<string,int>::iterator it = mp2.begin();it != mp2.end();it++)
{
cout << " mp2.first = " << (*it).first << "\t mp2.second" << (*it).second << endl;
}
}
void test02()
{
map<int, int> mp3;
//插入
//第一种
mp3.insert(pair<int, int>(5, 50));
//第二种
mp3.insert(make_pair(2, 20));
//第三种
mp3.insert(map<int, int>::value_type(3, 30));
//第四种 不常用,容易出问题。
mp3[100] = 10000;
printMap(mp3);
//当这里用mp3[200] 来查找key 为200的对组时,它会自动插入key为200 且value为0 的map
cout << mp3[200] << endl;
printMap(mp3);
}
void main()
{
test02();
}map查找和统计
功能描述:
- 对map 容器进行查找数据以及统计数据
函数原型:
find(key);//查找key 是否存在,若存在,返回该键的元素的迭代器;若不存在,返回map.end();count(key);//统计key的元素个数
map不允许插入重复key 元素,count统计而言,结果要么为0 要么为1;
multimap 的count统计可能大于1
Summary:
- find --- 返回是一个迭代器
- count 对于map 容器 要么是0,要么是1
#include <iostream>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
class myCompare {
public:
//注意形参列表后面一定要const 否则报错
bool operator()(int v1, int v2) const {
return v1 > v2;
}
};
// 这里的map 模板可以加myCompare,不加其实也行。
void printMap(const map<int, string,myCompare>& mp)
{
for (map<int,string,myCompare>::const_iterator it = mp.begin();it!=mp.end();it++)
{
cout << " (*it).first = " << (*it).first << " \t it->second = " << it->second << endl;
}
}
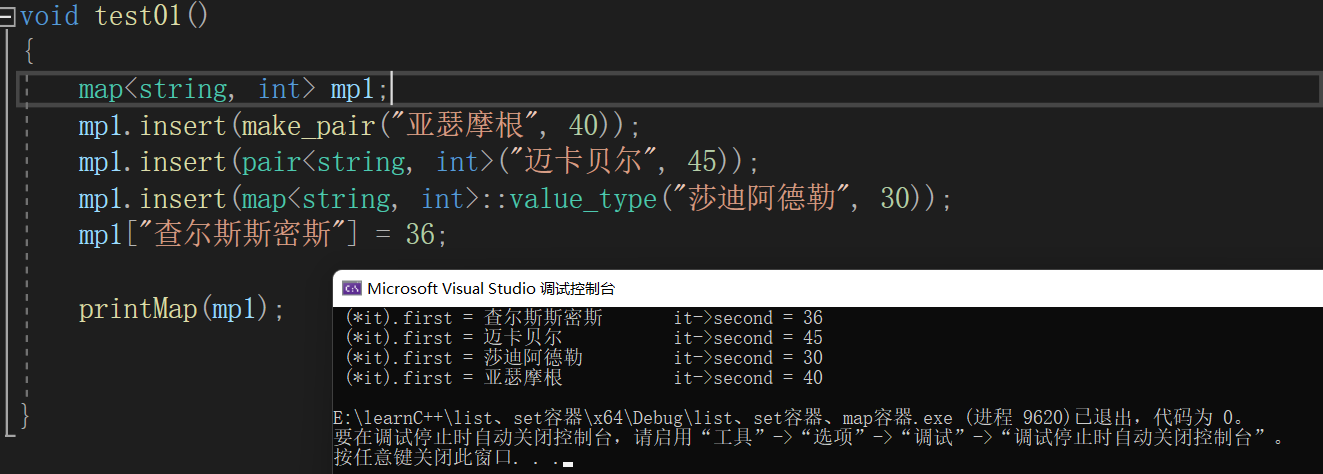
void test01()
{
map<int, string,myCompare> mp1;
mp1.insert(make_pair(40,"亚瑟摩根"));
mp1.insert(pair<int, string>(45,"迈卡贝尔"));
mp1.insert(map<int, string,myCompare>::value_type(30,"莎迪阿德勒"));
mp1[36] = "查尔斯斯密斯";
printMap(mp1);
//这里的map模板 没加 myCompare 也行。
for (map<int, string>::iterator it = mp1.begin();it != mp1.end();it++)
{
cout << " (*it).first = " << (*it).first << " \t it->second = " << it->second << endl;
}
}
void main()
{
test01();
}Ask:multimap如果有多个key那么返回的迭代器是哪一个呢?返回第一个,但是可以通过count()方法来找到它的区间。
Summary
- 利用仿函数可以指定 map 容器的排序规则
- 对于自定义数据类型, map 必须指定排序规则,同set容器。